how to draw 3d window in autocad
Basic 3D and Surface Modelling
Introduction
Although AutoCAD has a number of commands for creating special 3D objects, a lot can exist achieved past changing the properties of basic 2D objects like polylines. Most 2d objects can exist given a thickness using the thickness option in the Backdrop (DDCHPROP) command. Although objects with a thickness can be said to be extruded, this should not exist confused with the EXTRUDE command which creates solid extrusions; giving an object thickness produces a surface extrusion. All objects can be given an meridian by moving them in the Z management using the MOVE command. With a combination of the MOVE and Properties commands you can quickly create uncomplicated 3D drawings.
Using this tutorial you will acquire how to give objects a thickness, how to motion them vertically, how to view your 3D creations and how to utilize the 3DFACE and SHADE commands.
The DDVPOINT Command
Yous tin use this command to get an axonometric view of your drawing.
There are a number of ways to become an axonometric view of your AutoCAD drawing but the DDVPOINT command is probably the easiest and quickest to use. It is, however, buried ii layers deep in the pull-down menu so it's often quicker simply to blazon it at the keyboard, since at that place is no toolbar button. As you probably recognise from the command name it is a dialogue box driven control. The Viewpoint Presets dialogue box is illustrated on the right. As you lot can see, y'all define a view by specifying two angles. The kickoff angle is the rotation from the Ten axis (the horizontal angle). The second is the angle from the XY aeroplane (the vertical bending). Using the dialogue box you tin can specify an bending either by picking on the two dials or by inbound an angle into each of the 2 angle edit boxes. You can fifty-fifty look at your drawing from underneath past specifying a negative vertical angle. For nearly purposes a horizontal angle along 1 of the diagonals, 45, 135, 225 and 315 and a vertical angle of 30 give the best results.
You can render to a plan view of your drawing by using the Plan control. To do this, just enter "PLAN" at the control prompt and and so ![]() to accept the "Current UCS" default. You can too return to any previous view by using the Zoom Previous command option, Z
to accept the "Current UCS" default. You can too return to any previous view by using the Zoom Previous command option, Z ![]() P
P ![]() at the keyboard or
at the keyboard or ![]() from the Standard toolbar.
from the Standard toolbar.
Pinnacle of page
The Properties Command
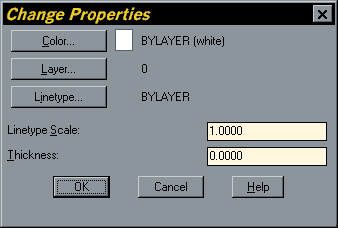
You tin use the DDCHPROP control to change the colour, layer, linetype, linetype scale and thickness of any single or multiple object selection. The DDMODIFY command gives all of these change options in addition to those which are specific to the object type. DDMODIFY is always used by AutoCAD every bit a default for unmarried object selections when the Properties control is selected from the toolbar or from the pull-down menu.

Command Sequence
Command: DDCHPROP
Select objects: (pick one or more objects)
Select objects: ![]()
When you have selected the objects, the Alter Properties dialogue box appears. To alter the thickness, simply enter a value (in cartoon units) in the Thickness edit box. When y'all click the "OK" push button your objects volition exist extruded by the amount specified.
The illustration (right) shows the result of applying a thickness to a circumvolve. A circumvolve with no thickness is shown on the left and a circumvolve with thickness on the right.
Effectively a circle with thickness becomes a cylinder. Y'all tin can tell by the orientation of the UCS icon in this illustration that this is an axonometric view (see "The DDVPOINT Command" above for details).
Moving in the Z Direction
Past now you should exist quite used to using the Move control only upwards until at present y'all've just been moving second objects in the XY Plane. Movement tin can only as hands exist used to motion a drawing object vertically, perpendicular to the XY Plane. You can practise this by using XY and Z co-ordinates or by picking points in 3D space.
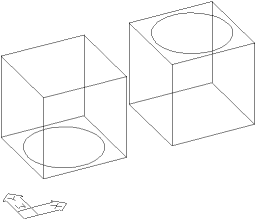 In the illustration on the left a circle has been moved from the base plane of a cube to the top face of a cube. This is done by using the Move command ( from the pull-downwards or
In the illustration on the left a circle has been moved from the base plane of a cube to the top face of a cube. This is done by using the Move command ( from the pull-downwards or ![]() from the Change toolbar). Just start the Movement control, select the circle, pick one of the lower corners of the cube every bit the base signal (use the end betoken Osnap!) and and then selection the corresponding acme corner equally the 2d bespeak, again using the end point Osnap. If you lot expect at the circumvolve in plan there appears to be no difference in information technology'south position because it has not been moved in the XY airplane but perpendicular to it. Y'all can use the same principle to move any drawing entity. Bear in mind that you must ever utilize an Osnap when you are picking points in 3D space. If y'all practice non, the picked point will always exist on the base aeroplane, which doesn't make whatsoever sense. I of the problems with this is that you may non realise your error until yous alter your view position because in the current view the objects will announced to have been moved usually. It'southward a good idea to keep switching your view signal as a check.
from the Change toolbar). Just start the Movement control, select the circle, pick one of the lower corners of the cube every bit the base signal (use the end betoken Osnap!) and and then selection the corresponding acme corner equally the 2d bespeak, again using the end point Osnap. If you lot expect at the circumvolve in plan there appears to be no difference in information technology'south position because it has not been moved in the XY airplane but perpendicular to it. Y'all can use the same principle to move any drawing entity. Bear in mind that you must ever utilize an Osnap when you are picking points in 3D space. If y'all practice non, the picked point will always exist on the base aeroplane, which doesn't make whatsoever sense. I of the problems with this is that you may non realise your error until yous alter your view position because in the current view the objects will announced to have been moved usually. It'southward a good idea to keep switching your view signal as a check.
In the higher up example the move was adequately like shooting fish in a barrel because we had a cube to use every bit a guide. Very often you will need to move an object vertically without whatever guide. In such a instance you should use co-ordinates. For case, if the cube in the illustration higher up was 40 drawing units loftier then I could motility the circle using the post-obit command sequence.
Command Sequence
Command: MOVE
Select objects: (select the circle)
Select objects: ![]()
Base of operations point or displacement: 0,0,0
Second point of deportation: 0,0,40
Observe that I utilize the UCS origin point as a base point, that'south because it'south standard practice but in principle it could be any point in space. The about important matter is that the X and Y co-ordinates remain the aforementioned (because we practise non want to motility in the XY Plane) and the Z according must increase by the distance yous want to motility upwardly. Using co-ordinate 25,43,sixteen as the base bespeak and 25,43,56 every bit the second point would have resulted in exactly the same motility. To motion downward you just need to specify a negative Z co-ordinate. For example to motion the circle down by 40 units the second point co-ordinate would be 0,0,-40.
Top of folio
The 3D Face Command
 The 3D Face command is used to draw 3D surfaces with three or iv edges.
The 3D Face command is used to draw 3D surfaces with three or iv edges.
Command Sequence
Command: 3DFACE
First Bespeak: (pick point)
2d Point: (pick betoken)
Third Point: (choice indicate)
Fourth Indicate: (pick betoken or ![]() for only three edges)
for only three edges)
Third Point: (get-go another 3D Face or ![]() to cease)
to cease)
Why do I need a 3D Face up?
The reason is that when yous requite an entity like a rectangle a thickness it is given solid sides in the direction of the extrusion just information technology is left open up concluded like a tube. To add a pinnacle and a bottom to a box y'all must use 3D Faces. In the illustration on the right, two boxes have been shaded using the Shade command, SHADE from the keyboard, from the pull-down or ![]() from the Return toolbar. See SHADE for a description of the Shade command options. The box on the right is a rectangle which has been given a thickness. Every bit you can see, it does not have a pinnacle. A 3D Face up has been added to the top of the box on the left which gives the event of a solid surface when shaded.
from the Return toolbar. See SHADE for a description of the Shade command options. The box on the right is a rectangle which has been given a thickness. Every bit you can see, it does not have a pinnacle. A 3D Face up has been added to the top of the box on the left which gives the event of a solid surface when shaded.
When you lot use the Shade command, don't forget to apply the Regen command to get back to the wireline cartoon. AutoCAD does not let you to pick points on a shaded drawing.
For complicated shapes you may need to use a number of 3D Faces to fill a surface. Fortunately, extruded circles are automatically given a solid elevation and lesser so you don't demand any 3D Faces. If yous do need to use a complex of faces to fill a surface there is a mode to hide the bring together lines between faces. If y'all type "I" and ![]() before the first pick point of whatever border, that edge volition exist made invisible. If you are conscientious y'all tin can easily fill a complicated surface with many 3D Faces which volition simply appear as a unmarried continuous surface. If you need to create a very complex surface it may be ameliorate to use the EXTRUDE command which creates solid extrusions i.east. they already accept pinnacle and bottom surfaces.
before the first pick point of whatever border, that edge volition exist made invisible. If you are conscientious y'all tin can easily fill a complicated surface with many 3D Faces which volition simply appear as a unmarried continuous surface. If you need to create a very complex surface it may be ameliorate to use the EXTRUDE command which creates solid extrusions i.east. they already accept pinnacle and bottom surfaces.
Meridian of page
An Do
The do beneath is designed so that you lot tin can practice all of the new commands and techniques outlined higher up. It is a elementary tabular array which is equanimous of 9 primary elements, four legs, 4 rails, and a tiptop. These elements are all constructed using the Rectangle command, RECTANG from the keyboard or from the pull-down menu. Retrieve, there is zip special nearly rectangles, they are just four sided closed polylines, and then if you lot prefer using the PLINE command, then feel free.
These rectangles will be given a thickness using the Properties control and an tiptop using the MOVE command. Some 3D Faces are used for the finishing touches using the 3DFACE command.
Height of page
Drawing the Table
Step ane
Showtime of all draw the table plan using the dimensions on the illustration and inset particular below. All dimensions are in millimetres. The plan is composed of nine rectangles. You may demand to utilize other commands like Line ![]() and Offset
and Offset ![]() to construct the rectangles. Alternatively yous can work out the rectangle co-ordinates and construct them manually. Remember to use the Copy
to construct the rectangles. Alternatively yous can work out the rectangle co-ordinates and construct them manually. Remember to use the Copy ![]() and/or Mirror
and/or Mirror ![]() commands to duplicate identical objects. For example, it's actually only necessary to depict 1 leg since they are all the same.
commands to duplicate identical objects. For example, it's actually only necessary to depict 1 leg since they are all the same.
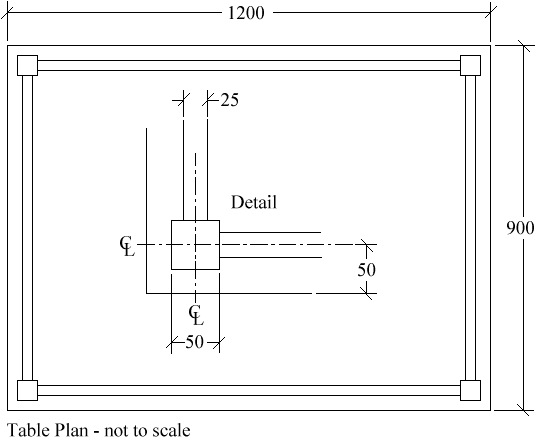
Step 2
Next, using the Properties ![]() command, select the four table legs and give them a thickness of 700. Using the Backdrop command a second time, select the 4 table rails and requite them a thickness of 100. Movement the rail vertically through 600 with the MOVE
command, select the four table legs and give them a thickness of 700. Using the Backdrop command a second time, select the 4 table rails and requite them a thickness of 100. Movement the rail vertically through 600 with the MOVE ![]() command using a co-ordinate value of 0,0,0 for the base of operations point and 0,0,600 for the second point. Finally use the Properties command a third fourth dimension to give the table top a thickness of 40 and use Motion again to requite the top an elevation of 700. Now look at what you take created using the DDVPOINT command, from the pull-down or DDVPOINT at the keyboard. Apply the SHADE
command using a co-ordinate value of 0,0,0 for the base of operations point and 0,0,600 for the second point. Finally use the Properties command a third fourth dimension to give the table top a thickness of 40 and use Motion again to requite the top an elevation of 700. Now look at what you take created using the DDVPOINT command, from the pull-down or DDVPOINT at the keyboard. Apply the SHADE ![]() command to see the solid event, from the pull-downwards or SHADE at the keyboard.
command to see the solid event, from the pull-downwards or SHADE at the keyboard.
Step three
Equally you lot will have noticed, your table does not still have a solid top. Y'all tin reach this using 3D Face up. You tin can first the 3D Face up command from the pull-down, , from the Render toolbar, ![]() or from the keyboard, 3DFACE. 3D Faces are defined by picking the four points of a rectangle in either a clockwise or anticlockwise management. Start the 3D Face command and using the endpoint Osnap, select the four upper corners of the tabular array meridian. Utilise the Shade command once more to see the effect. You can use more 3D Faces to complete the model. By looking at the table from diverse angles y'all will notice that the underside of the rails, the underside of the legs and the underside of the tabular array summit all need 3D Faces in order to create a completely solid model.
or from the keyboard, 3DFACE. 3D Faces are defined by picking the four points of a rectangle in either a clockwise or anticlockwise management. Start the 3D Face command and using the endpoint Osnap, select the four upper corners of the tabular array meridian. Utilise the Shade command once more to see the effect. You can use more 3D Faces to complete the model. By looking at the table from diverse angles y'all will notice that the underside of the rails, the underside of the legs and the underside of the tabular array summit all need 3D Faces in order to create a completely solid model.
At present that you accept completed your model, experiment with the Shade command and the various shade border settings (run across "Tips and Tricks" below).
Step 4
To finish your drawing, set up tilemode to 0, create an A3 drawing sheet and insert some tiled viewports, come across thePaper Space exercise for details. Your drawing should end upward looking something like the i beneath. The vase was created using the REVSURF control, run into REVSURF for details.
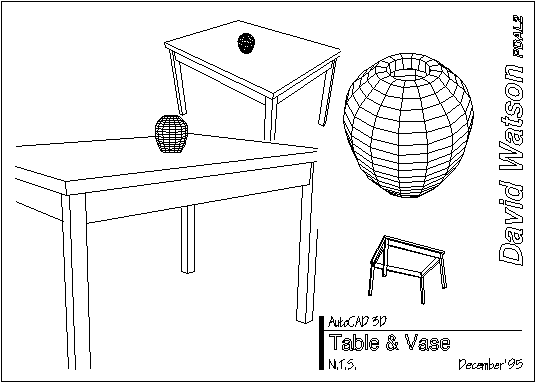
Top of page
3D Objects
In add-on to the simple 3D objects you tin create by giving objects thickness and adding 3D Faces, AutoCAD provides a number of ready made 3D objects. These objects can exist chosen from the 3D Objects dialogue box. Every bit you can see from the illustration of the dialogue box below, you tin can create very simple objects like a box and complex ones like the torus.
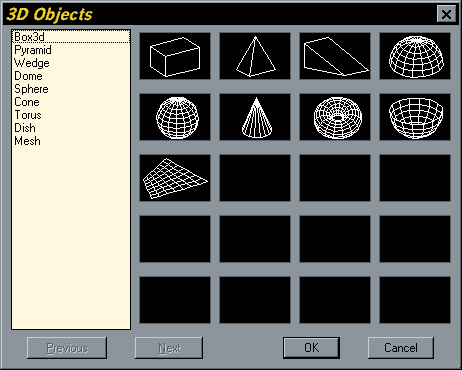
You must invoke the 3D objects dialogue box from the pull-down bill of fare, equally there is no keyboard equivalent. Alternatively you can select individual 3D Object commands from the Surfaces toolbar. Each 3D Object requires different input from the user but the command line is quite explicit then you shouldn't have any problems.
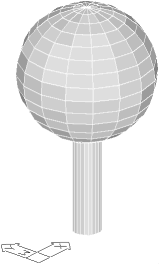 One of the nearly useful objects is the Sphere. In the illustration on the right a 3D tree has been created using a circumvolve with thickness every bit the trunk and a sphere as the awning. One thing to carry in mind when creating spheres is that the centre of the sphere will be on the basis plane. Therefore, half of the sphere is below ground level and half in a higher place. If you desire the sphere to sit on the ground plane, all you take to practise is movement information technology up through a altitude which is the same every bit it'south radius.
One of the nearly useful objects is the Sphere. In the illustration on the right a 3D tree has been created using a circumvolve with thickness every bit the trunk and a sphere as the awning. One thing to carry in mind when creating spheres is that the centre of the sphere will be on the basis plane. Therefore, half of the sphere is below ground level and half in a higher place. If you desire the sphere to sit on the ground plane, all you take to practise is movement information technology up through a altitude which is the same every bit it'south radius.
Another consideration when creating spheres and some of the other shapes is the number of segments to utilize. It is very tempting to apply a lot and create a smooth shape but this does take lots of drawing retentivity so go carefully. The default value (16) is commonly acceptable for most purposes.
Command Sequence
Invoke the dialogue box from the pull-down (), choice the sphere icon and so the "OK" push button or pick ![]() from the Surfaces toolbar.
from the Surfaces toolbar.
Center of sphere: (option point)
Diameter/<radius>: (pick point or enter value)
Number of longitudinal segments<sixteen>: (enter number or![]() )
)
Number of latitudinal segments<sixteen>: (enter number or![]() )
)
Your Sphere is drawn.
Meridian of page
Tips & Tricks
- If y'all would like to try creating the vase as shown in the table drawing. You will need to know a little bit about UCS, User According Systems (see UCS) and how the Revolved Surface command works (run into the 3D Tree do for details).
- You lot tin can change the shaded effect that the Shade command gives to your drawing using the SHADEDGE variable. To alter the shade edge variable just enter SHADEDGE at the keyboard and enter a value between 0 and three.
SHADEDGE = 0 gives a shaded colour surface with no lines.
SHADEDGE = one gives a shaded colour surface with lines. This tends to requite the all-time overall results.
SHADEDGE = ii gives a background colour surface which gives a similar effect to the Hide command.
SHADEDGE = three gives a cake colour surface, this is the AutoCAD default. See SHADE for a fuller clarification of the SHADEDGE variable. - Always use Osnaps when picking in 3D.
- Apply the Shade command regularly to keep track of your drawing. In wireline it's impossible to tell if a surface has a 3D Face or non, so you'll need to apply Shade to check.
- Y'all can force invisible 3D Confront edges to display in wireline using the SPLFRAME variable. If SPLFRAME = 0 all invisible edges remain subconscious. If it is fix to ane invisible edges will exist displayed. This can be extremely useful considering information technology is impossible to select a 3D Face which has no visible edges. The but way to select such a 3D Face is to set SPLFRAME to 1 first.
Top of page
Donate to CADTutor
If you establish this tutorial useful, you might similar to consider making a donation. All content on this site is provided complimentary of charge and we hope to keep it that way. However, running a site like CADTutor does cost money and you tin help to improve the service and to guarantee its future by altruistic a minor amount. Nosotros gauge that you probably wouldn't miss $five.00 but it would make all the difference to united states of america.
Source: https://www.cadtutor.net/tutorials/autocad/basic-3d.php
0 Response to "how to draw 3d window in autocad"
Post a Comment